Mitigating Rogue Trading with Governance, Controls, and Reporting Systems
In the corridors of high finance, certain traders stand out not just for their skills. These individuals often occupy pivotal positions within their firms, granting them access to sensitive information and significant trading power. Under pressure to deliver consistent profits, their actions are rarely overt; instead, they weave a web of small deceitful decisions that go unnoticed until the damage is irreparable.
The environment in which these traders work is typically one of intense pressure and high expectations, where success is measured by short-term gains and personal reward. Employers, driven by the demand for impressive performance, may inadvertently create fertile ground for reckless behavior by prioritising results over strict compliance. Ultimately, it is a combination of personal ambition, a permissive corporate culture, and the ability to operate undetected for a period of time that makes these traders uniquely risky assets for their employers.
In the world of financial trading, rogue trading remains a significant operational risk, often leading to catastrophic losses when left unchecked. As financial institutions continue to grow in complexity and trading environments evolve, mitigating these risks requires robust governance, enhanced internal controls, and effective reporting systems. In this follow-up article, we explore the practical steps that organizations can implement to reduce the likelihood of rogue trading and mitigate its impact, based on established regulatory guidelines and operational risk management frameworks.
The Root Causes of Rogue Trading
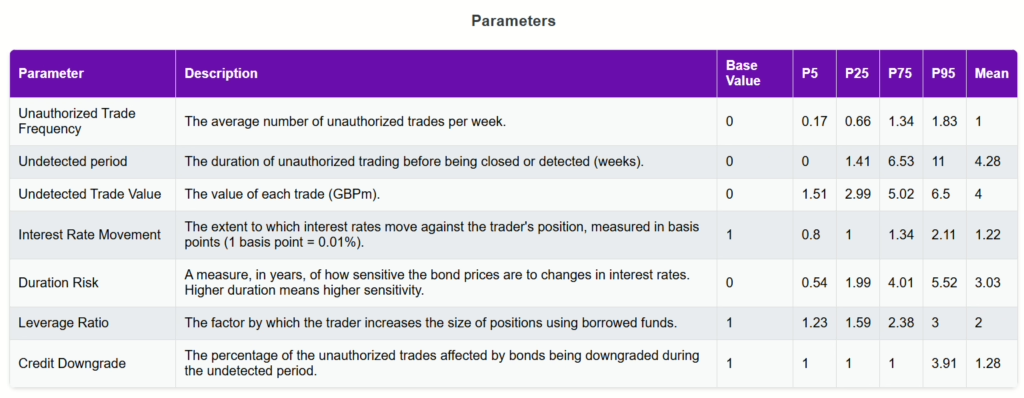
Rogue trading often arises when unauthorized trades bypass internal controls, leverage is misused, or trading operations are poorly monitored. The infamous case at Société Générale in 2008, where a rogue trader caused billions in losses, highlighted the potential for disaster when governance mechanisms and risk controls fail. Key factors contributing to rogue trading incidents include:
Lack of oversight and governance at senior levels
Inadequate separation of duties between the front, middle, and back offices
Weak internal control mechanisms
Ineffective reporting and early-warning systems
To mitigate these risks, financial institutions must adopt a comprehensive approach that integrates robust governance structures, stringent control measures, and real-time reporting mechanisms.
Key Mitigation Strategies
While Monte Carlo simulation provides valuable insights, it functions as one component of a comprehensive control framework:
| Primary Controls | Secondary Controls |
|---|---|
|
|
The simulation results should inform the calibration of these controls. For example, if simulations show potential for rapid loss escalation under certain conditions, institutions might:
| Control | Description |
|---|---|
| Independent risk oversight | Establish an independent risk management function to provide oversight and challenge on risk-taking activities. |
| Lower position limits | Reduce the maximum positions that traders can hold to limit the potential for outsized losses. |
| Increase margin requirements | Require traders to post higher levels of margin to cover their positions, reducing the leverage in the system. |
| Enhance monitoring frequency | Increase the frequency of position monitoring and reconciliation to identify potential issues more quickly. |
| Implement additional approval layers for specific product types | Introduce additional layers of approval and oversight for complex or higher-risk products. |
1. Strengthening Governance Mechanisms
At the heart of effective risk management lies strong governance. Senior management must have a full understanding of both the potential and actual operational risks posed by market-related activities, particularly within trading desks. Governance measures should ensure:
Clear segregation of duties between the front office (trading), middle office (risk management), and back office (settlements and accounting). This separation helps prevent unauthorized actions by ensuring that no one individual has control over the full trade lifecycle.
Committees with risk oversight roles should be established. These committees must have adequate resources to challenge front-office activities and ensure that any suspicious trading behavior is addressed immediately.
Promotion of a risk-aware culture within the trading environment is also critical. Traders should operate under clear terms of reference, with frequent reviews and escalation procedures in place to investigate breaches of trading limits.
Governance frameworks that promote transparency, accountability, and high professional standards in trading environments provide a critical first line of defense against rogue activities.
2. Enhancing Internal Controls
Robust internal controls are essential for detecting and preventing unauthorized trading activities. Institutions should implement the following controls across all trading desks:
Rigorous trade confirmation, reconciliation, and settlement processes: All trades should be immediately reported and confirmed by the middle or back office, ensuring that any discrepancies are identified early. Confirmation processes should occur independently of the front office to reduce the risk of manipulation.
Mandatory “desk holidays” for traders: Requiring traders to take at least two consecutive weeks away from their desk annually allows a fresh set of eyes to review their books, making it harder for fraudulent behavior to go undetected.
Real-time monitoring of leverage and credit limits: Since rogue trading often involves excessive leverage, institutions should implement real-time systems to track positions and prevent breaches of set limits. Large trades or deviations from normal trading patterns should trigger automatic alerts for immediate investigation.
Additionally, audit trails documenting every step of a transaction—from initiation to settlement—enable institutions to maintain transparency and accountability, ensuring that even minor errors are traceable and correctable.
3. Improving Reporting and Early-Warning Systems
Early detection of rogue trading relies heavily on effective reporting systems. Institutions must establish internal reporting structures that can identify and escalate material incidents quickly:
Comprehensive risk reporting systems should generate real-time alerts when trading patterns deviate from expected norms. Whistle-blowing mechanisms should also be in place to allow staff to report suspicious behavior without fear of retribution.
Daily profit and loss (P&L) and position reconciliations: These reconciliations are critical for spotting unusual spikes or anomalies in trading activities, which may indicate rogue behavior. Random checks on trades, combined with analysis of key risk indicators, allow for rapid intervention before losses accumulate.
Regular fraud testing and scenario analysis: Institutions should periodically test their systems for vulnerabilities to fraud and rogue trading. By conducting scenario analyses, organizations can better understand where and how fraudulent behavior might emerge, enabling them to adjust their controls accordingly.
Moreover, reports should be well-structured, clear, and escalate issues in real-time to relevant control functions and senior management, ensuring that corrective action is taken swiftly.

Fraud Prevention and Detection: A Critical Element
Given the complexity of modern financial markets, the potential for both internal and external fraud has risen sharply. Institutions must actively integrate fraud detection into their operational risk frameworks. This can be achieved by:
Developing a fraud risk mapping program: By mapping potential fraud risks within trading activities, institutions can better prepare their systems to detect anomalies.
Increased fraud awareness training for all staff involved in trading and settlements. This ensures that individuals at every level understand their role in preventing and reporting fraudulent activity.
Rigorous testing and monitoring of fraud prevention systems, ensuring that they can handle the scale and complexity of modern trading environments.
Conclusion: Building Resilience Against Rogue Trading
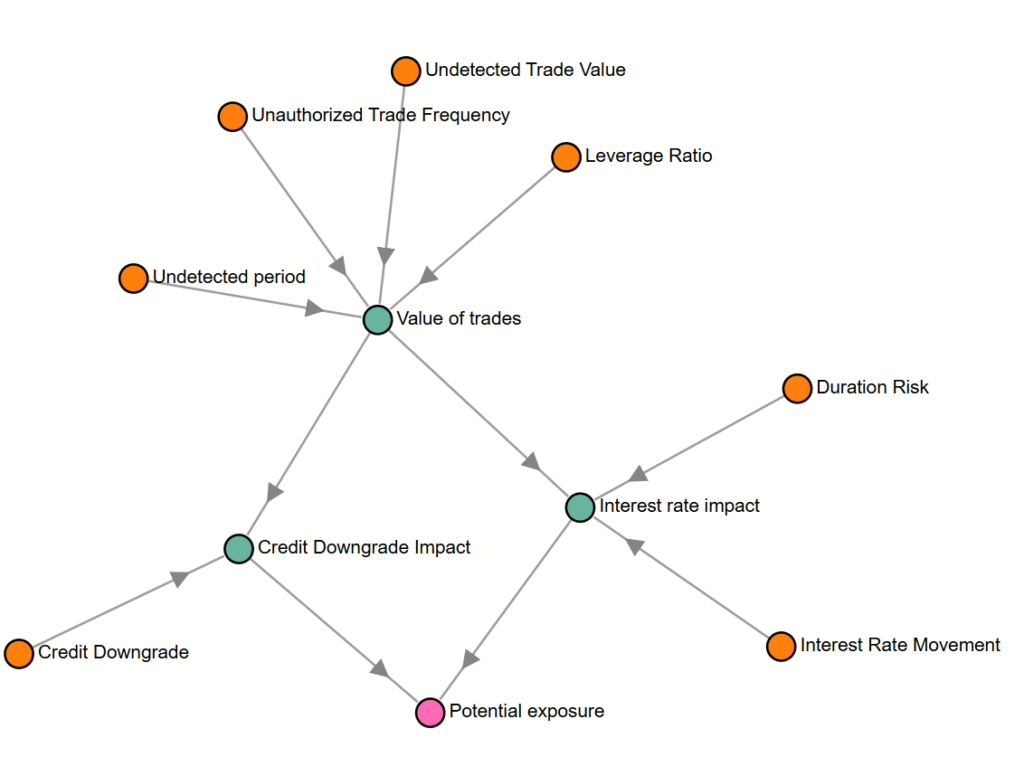
Mitigating the risks associated with rogue trading requires more than just compliance with basic regulations—it demands a proactive, integrated approach that encompasses governance, controls, and reporting systems. Monte Carlo simulations can help quantify potential exposures, but real-time governance and control mechanisms are essential for preventing these exposures from materializing into actual losses.
Financial institutions must prioritize the development of a risk-aware culture, enforce clear segregation of duties, and leverage advanced technology to detect and respond to anomalies in trading activities. By doing so, they can reduce the likelihood of rogue trading incidents and limit their impact if they do occur.
In an industry where operational risks are ever-evolving, institutions that strengthen their internal frameworks are better positioned to protect both their reputations and their bottom lines.
For further insights: Guidelines on management of operational risk in trading areas (europa.eu)