In today’s regulatory landscape, financial institutions are expected to maintain airtight compliance processes, especially when it comes to critical reports like Suspicious Activity Reports (SARs) required under anti-money laundering (AML) regulations. However, as demonstrated by recent simulations, even slight lapses in data aggregation or internal communication can lead to significant regulatory consequences. In this article, we will explore an operational risk scenario where Monte Carlo simulations shed light on the potential fallout of incomplete SAR filings. We’ll look at how this advanced risk modeling technique helps institutions prepare for the unexpected and mitigate costly risks.

Understanding the Scenario: Incomplete SARs and Regulatory Fallout
Imagine a bank that operates across various divisions—retail, high-net-worth (HNW) individuals, and treasury. Each of these divisions generates transaction data that needs to be aggregated and analyzed to detect suspicious activity. But what happens when the system responsible for aggregating this data misses certain high-risk patterns?
In this scenario, faulty data aggregation and miscommunication between the IT and compliance teams led to SARs being filed with incomplete information. While the IT team had identified the issue, the problem was never escalated to the compliance team, who continued to submit these incomplete reports. A regulatory audit, such as an S166 review by the Financial Conduct Authority (FCA), later revealed this critical failure.

Key Insights from the Monte Carlo Simulation
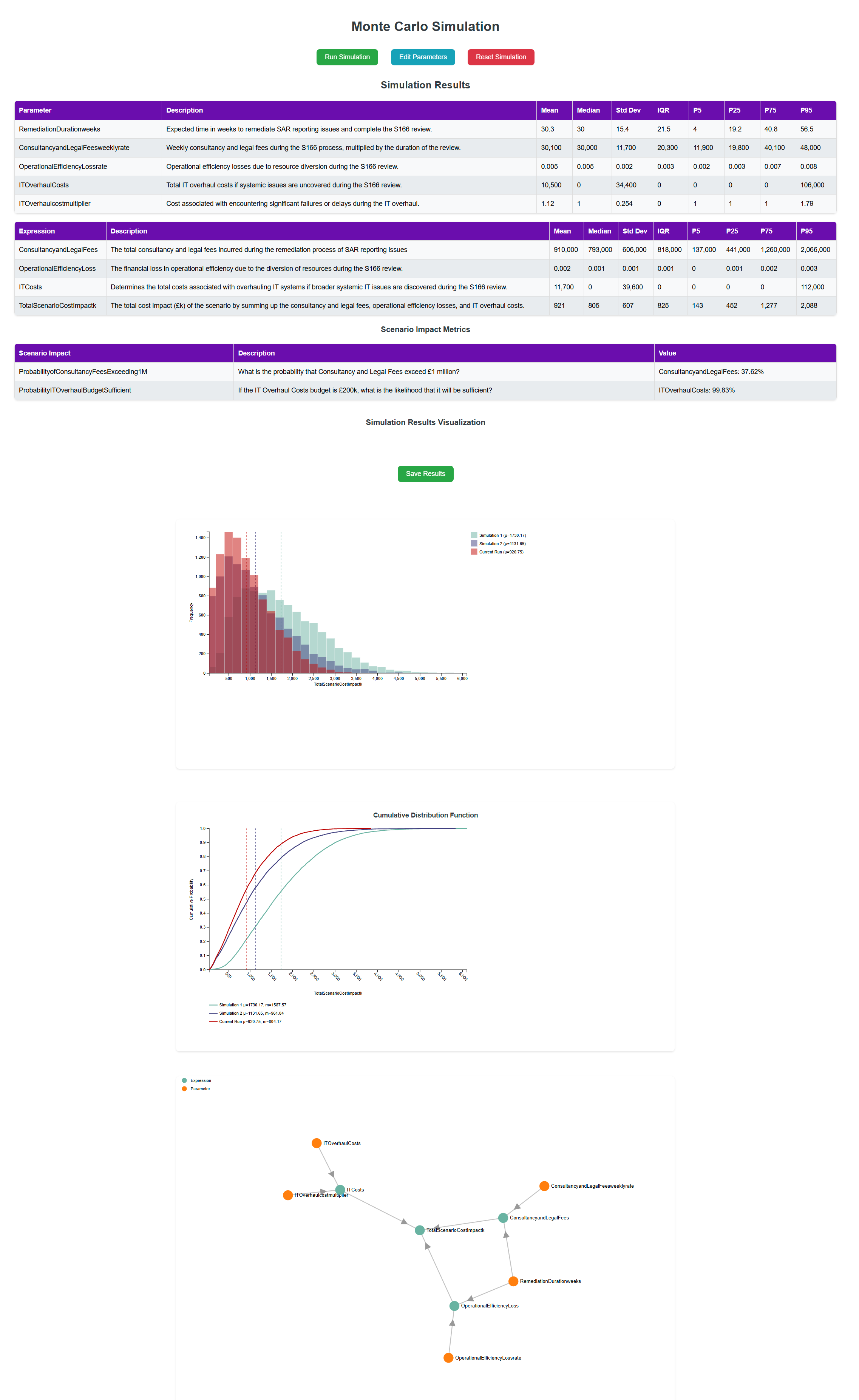
Monte Carlo simulations are invaluable tools for understanding how these operational failures can impact an institution. The dataset modeled several parameters to predict the cost and duration of remediation, potential efficiency losses, and the likelihood of uncovering deeper systemic issues. Here are the significant takeaways:
- Remediation Duration: The simulation showed a remediation timeline ranging from 12 to 78 weeks, with an average of 26 weeks, depending on the severity of the failure. This wide range reflects the uncertainty in resolving such complex IT and communication issues.
- Cost Implications: Weekly consultancy and legal fees during the review were estimated between £10,000 and £50,000, with a mean of £20,000. Over the course of a potential 26-week remediation period, this could add up to nearly £500,000. The possibility of an IT overhaul—should systemic issues be discovered—could drive costs even higher, reaching a mean estimate of £1,000,000, with a 20% likelihood of overruns adding an additional 50%.
- Operational Efficiency Loss: During the remediation process, the bank could face operational efficiency losses between 0.017% and 0.083%, small percentages that could nonetheless impact profitability over the long term. These losses stem from the diversion of resources towards resolving the regulatory breach rather than focusing on core business operations.
- Systemic IT Issues: There’s a 30% chance that the S166 review could uncover broader systemic IT issues, requiring a significant overhaul. This introduces additional layers of risk, both in terms of operational disruptions and unexpected financial costs.

Breaking Down the Cost Drivers: Key Expressions in the Simulation
The Monte Carlo simulation provides a powerful lens through which to examine how various factors combine to determine the overall financial impact of this operational risk event. Below are the key expressions that model the event’s cost dynamics.
- Consultancy and Legal Fees
Formula: Consultancy and Legal Fees weekly rate * Remediation Duration weeks
Mean value: £1.6 million (range: up to £3.1 million)
Key Insight: The S166 review is anticiplated to last around 51 weeks, and the weekly cost is modeled at a mean rate of £31,000. In a 1-in-20 scenario, this cost could reach £3.1 million. The length of the review significantly influences the financial impact. - Operational Efficiency Loss
Formula: (Operational Efficiency Loss rate / 100) * Company revenue * Remediation Duration weeks
Mean value: £760,000 (range: up to £1.6 million)
Key Insight: A minor operational efficiency loss during the review has a significant impact on the bottom line. At a rate of 0.5% (mean) of the bank’s £300 million annual revenue, this loss accumulates to around £760,000. In a 1-in-20 scenario, where losses peak at 0.8%, the total efficiency loss could rise to £1.6 million. Small inefficiencies, when compounded over time, can create significant financial stress. - IT Overhaul Costs
Formula: IT Overhaul Costs * IT Overhaul cost multiplier
Mean value: £230,000 (range: up to £1.6 million)
Key Insight: If systemic IT issues are uncovered during the review, the overhaul could be costly. Because of the considerable uncertainty around IT overhaul costs, we introduced the multiplier, which suggests costs could rise by nearly 80% and could exceed £1.6 million. - Total Scenario Cost Impact
Formula: Consultancy and Legal Fees + Operational Efficiency Loss + IT Overhaul Costs
Mean value: £2.5 million (range: up to £4.8 million)
Key Insight: Combining all the cost elements, the total scenario cost impact averages around £2.5 million. In a 1-in-20 event, this figure could rise to £4.8 million, showing the importance of preparing for low-probability but high-impact operational events.
The Power of Simulation: Small Efficiency Losses, Big Financial Impact
One of the most striking results of this simulation is how a seemingly small operational efficiency loss—modeled at a rate of 0.5%—translates into substantial financial consequences. This finding underscores the hidden costs of operational disruptions. For a company that processes millions of transactions and generates significant annual revenue, small inefficiencies compound rapidly over time, draining profits that would otherwise be reinvested into growth or innovation.
The IT Overhaul Cost Multiplier: Amplifying Financial Risk
Another key variable in the scenario is the IT overhaul cost multiplier, which introduces a layer of uncertainty around the potential expenses tied to IT failures. This multiplier reflects the likelihood that unanticipated technical difficulties or delays will drive up costs beyond initial estimates.
What’s particularly important about the multiplier is its amplifying effect on uncertainty. The base cost assumption is already significant, but the potential for it to double in the event of IT failures makes this a critical area of focus for further evaluation.
Real-World Implications for Financial Institutions
This scenario also emphasizes the importance of proactive risk management. Identifying potential system failures early, improving communication between IT and compliance teams, and investing in robust IT infrastructures are all strategies that can mitigate the risk of costly regulatory reviews and operational inefficiencies.
The findings underscore the ripple effect that overlooked errors in compliance reporting can have on a financial institution. A remediation process that takes upwards of a year, coupled with escalating consultancy fees and potential systemic IT issues, can lead to significant operational and financial strain.
More importantly, the Monte Carlo simulation helps quantify these risks, providing management with a clearer view of the potential costs and timelines involved. This empowers decision-makers to prioritize resources effectively, reduce inefficiencies, and ensure that their compliance frameworks are robust enough to avoid such regulatory pitfalls.
The Broader Context: A Growing Need for Advanced Risk Management
Monte Carlo simulations, long a staple in financial modeling for market risk, are now proving their value in operational risk as well. Beyond the financial services sector, industries such as manufacturing and logistics are also adopting these techniques to optimize their risk management strategies, demonstrating the versatility and growing relevance of simulation-based approaches.
Adopting a data-driven scenario approach can provide the foresight needed to navigate complex environments and avoid costly oversights. Whether you are in financial services or another industry, now is the time to integrate simulation-based approaches into your operational risk management strategy.
Closing Thoughts: In an era where compliance missteps can cost millions and undermine a firm’s reputation, leveraging Monte Carlo simulations can mean the difference between reactive firefighting and proactive risk mitigation. Are you ready to take your risk management to the next level?
